Vitamin D3 Benefits
Vitamin D3, also known as the “sunshine vitamin,” is one of many nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. This fat-soluble vitamin is unique because our bodies can produce it in response to sunlight exposure. Today, I want to talk about Vitamin D3 Benefits.
Please note, I’m not a nurse, doctor, or anyone in the medical field. Please check with your medical professional to be sure Vitamin D3 is right for you and that any dose you take is appropriate. This is what I use, Vitamin D3. (Softgels)

The Role of Vitamin D3 in Bone Health
Calcium Absorption
One of the primary functions of vitamin D3 is to enhance the body’s absorption of calcium in the small intestine. Calcium is a key mineral essential for the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth. Without adequate levels of vitamin D3, the body struggles to absorb calcium efficiently, leading to potential issues like osteoporosis and bone fractures. 16 Plants You Can Eat When You’re Desperate for Food
Bone Mineralization
Vitamin D3 is instrumental in bone mineralization, a process crucial for bone density and strength. It helps regulate the levels of calcium and phosphorus in the bloodstream, ensuring that these minerals are available for the formation of bone tissue. Insufficient vitamin D3 can compromise this process, resulting in weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures due to poor bone health. As we age, having healthy bones is critical to our overall body health. Symptoms of a Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D3 and Immune Function
Immune System Modulation
Emerging research suggests that vitamin D3 plays a vital role in modulating the immune system. Adequate levels of vitamin D3 are associated with a lower risk of infections and a more robust immune response. Maintaining the necessary vitamin D3 level is believed to enhance the innate immune system’s ability to defend against pathogens, contributing to overall immune resilience. How to Boost Your Immune System
Autoimmune Conditions
Low vitamin D levels in the body have been linked to an increased susceptibility to autoimmune conditions. Studies have shown correlations between vitamin D deficiency and conditions such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Having enough vitamin D3 may help mitigate the risk of autoimmune disorders. Autoimmune Disease: What You Need to Know
Vitamin D3 and Mental Health
Mood Regulation
Beyond its physical benefits, vitamin D3 is implicated in mood regulation and mental well-being. Research suggests a connection between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of mood disorders such as depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Exposure to sunlight, which stimulates vitamin D3 production, is often recommended as part of strategies to alleviate symptoms of these conditions. How to Be Tougher Mentally As a Prepper
Cognitive Function
Some studies indicate that vitamin D3 may play a role in cognitive function and the prevention of neurodegenerative disorders. While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, maintaining optimal vitamin D3 levels appears to be associated with better cognitive health and a reduced risk of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. Mental Health Issues After A Disaster
Sources of Vitamin D3
Sunlight Exposure
The most natural way to obtain vitamin D3 is through exposure to sunlight. When UVB rays from the sun interact with the skin, a precursor molecule is converted into active vitamin D3. However, factors such as geographic location, skin pigmentation, and sunscreen use can influence the amount of vitamin D3 produced through sunlight exposure. Harnessing Sunlight for Emergency Preparedness
Dietary Sources
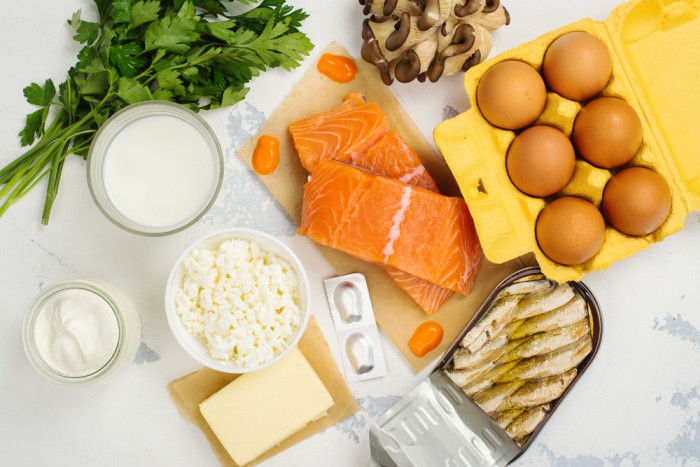
While relatively few foods naturally contain vitamin D3, some dietary sources can contribute to its intake. Fatty fish (such as salmon, tuna, sardines, and mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified foods like dairy products and cereals can provide supplemental vitamin D3.
However, it can be challenging to obtain sufficient levels through diet alone, especially for individuals with specific dietary restrictions. To get all the vitamin D you need it may be necessary to have some vitamin D supplementation. You can research to see how much vitamin D you need based on your age, sex, and body size. There are charts showing the International Units (IU) recommended. 10 Meals to Make When You’re Low on Food
Vitamin D3 Deficiency and Supplementation
Common Risk Factors
Vitamin D3 deficiency is a global health concern, and certain populations are more susceptible. Those at higher risk include individuals with limited sun exposure, older adults, people with darker skin, and those with conditions that impair fat absorption, such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disorders. Types of Medicines You Need for a First Aid Kit
Supplementation Benefits
For individuals at risk of deficiency, vitamin D3 supplementation is a viable option. Supplements come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid drops. It is important, however, to consult with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, as excessive vitamin D intake can have adverse effects. Best Supplements to Stock
Some foods to consider eating to help maintain good levels of vitamin D include cod liver oil, egg yolk, yogurt, orange juice, cheese, and other highly fortified milk products.
As mentioned, be sure to check with your healthcare professional before starting any new vitamin D supplementation regimen. Most sources suggest 600 IU per day for adults 70 or younger and 800 IU for older adults. Most people can deal with 4,000 IU per day, but when approaching 10,000 or more, you could experience toxicity.
Are there risks to your body if you have too much vitamin D?
The main challenge to having too much vitamin D is that it can lead to high levels of calcium in your blood. Some of the physical symptoms of vitamin D toxicity people experience are nausea and vomiting, muscle weakness, and frequent urination. People have been known to have kidney issues like kidney stones and even kidney failure in extreme situations.
The nausea and vomiting could affect your body’s fluid levels and lead to dehydration. High levels of vitamin D3 have been shown to cause high blood pressure in some individuals. Of course, high blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to heart disease, heart attack, and stroke over time.
Some other frequently experienced issues from too much vitamin D include loss of appetite, hearing problems, being dizzy and disoriented, bowel problems like constipation, and extreme thirst.
More Tips
- 16 Plants You Can Eat When You’re Desperate for Food
- Vitamin B12: Everything You Need to Know
- Is Vitamin C Really Good for You?
- Why Vitamin D May Be Just What You Need
Final Word
Vitamin D3 benefits are an important part of overall well-being, influencing bone health, immune function, and mental stability. Its multifaceted roles make it essential for maintaining a robust and resilient body. Whether obtained through sunlight exposure, dietary sources, or supplementation, ensuring adequate vitamin D3 levels is a proactive step toward promoting optimal health and preventing various health conditions. May God Bless this World, Linda
Copyright Images: Vitamin D Natural Sources Depositphotos_166843104_S by Happy_lark, Vitamin D Products Depositphotos_382157696_S by NewAfrica




















If you live up north, you should definitely check with your doctor about a vitamin D supplement. I am not positive about this, (a question for your doctor) but I think sunscreen interferes with your body’s absorption of vitamin d.
Hi Janet, I have heard that as well. I have a daughter with Multiple Sclerosis and she has to get checked all the time for her Vitamin D levels. We had no idea the lack of sunshine was making it worse. Linda
I have struggled with low Vitamin D levels for years. The first time my current doctor checked my levels my Vitamin D was at 7, she likes to see the level at 80. It literally took years to get my level above 50. The thing that has made a difference for me was a sublingual Vitamin D3. It’s a tiny little pill that dissolves under your tongue. It worked better than the prescription strength Vit D3. If you have low Vitamin D levels, talk to your doc about the sublingual ones. As a bonus, they are a lot less expensive than the capsules.
Hi Topaz, wow, that was very low!!! I love hearing about the sublingual ones, great tip! Years ago, I had no idea how important Vitamin D was to our health. Or at least my doctor told me that. Glad you got yours to come up! Linda
I’ve been on Vit D supplements for 10+ years, ever since I was diagnosed with a severe deficiency and parathyroid disease. I’m at normal levels now. I am Norwegian and have very fair skin. I grew up on a ranch and had my fair exposure to the sun which resulted in melanoma (in situ) eventually. I avoid the sun like a vampire now! My husband and I heard, only once, during the pandemic that Vit D was a major key to not catching covid…and we never did. Hmmm, I wonder how much truth was to that?
Topaz, I have a daughter that can’t asorb Vit D pills. She takes an emulsion drop each day instead and it’s made it so she can get her levels up to normal. We just buy them off Amazon.
Hi Robbie, I’m glad your levels are better!! Wow, Melanoma is serious stuff, my friend! Yes, stay out of the sun! Linda
Hey Linda et al: Here is a very interesting and informative article that was just published on Early-Onset Dementia and Vit. D3 supplementation:
Best to all,
HI JOyce, oh that’s a good one! Thank you, Linda
HI Joyce, unless you are a member it won’t let you read it. I will have to delete the link. Darn, I tried to open it but it wants me to pay. I’ve been wanting to join it, but haven’t gotten around to it. I’m so sorry, Linda
Hello, Linda et al.: Here is an excerpt from the article I left a link for earlier. I am sorry that Epoch Times did not allow you to read the entire thing, but this part is really good:
(About early-onset dementia.)
“Major contributing risk factors included alcohol abuse, stroke, and hearing impairment—all previously identified as risks for cognitive decline.
However, the study also identified some additional risk factors associated with early-onset dementia that have not been previously explored in depth, including vitamin D deficiency, high levels of inflammatory C-reactive proteins, specifically in women, orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure that happens when standing after sitting), and social isolation.
Vitamin D Reduced Dementia Risk by 40 Percent
Previous epidemiological studies have also linked vitamin D deficiency with an increased risk of dementia, Claire Sexton, senior director of scientific programs and outreach at the Alzheimer’s Association, told The Epoch Times.
RELATED STORIES
Drinking These 3 Types of Beverages Increases the Risk of Dementia
1/4/2024
Drinking These 3 Types of Beverages Increases the Risk of Dementia
Sedentary Behavior Linked to Dementia and Shortened Lifespan: 4 Exercises Can Help
1/2/2024
Sedentary Behavior Linked to Dementia and Shortened Lifespan: 4 Exercises Can Help
However, relatively few studies have specifically examined risk factors for young-onset dementia, making Ms. Hendriks’s team’s study “a welcome addition to the literature,” Ms. Sexton said.
One relevant study, published in the Alzheimer’s Association’s journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, compared dementia onset between people who took vitamin D supplements and those who did not. The study included 12,388 Americans without a dementia diagnosis at baseline, with an average age of 71.
The study found that among those who developed dementia within 10 years, about 75 percent were non-supplement takers compared to only 25 percent who took vitamin D supplements. Supplementation provided greater protection for women, though it reduced dementia risk in both sexes.
Interestingly, the study found that vitamin D seemed to offer more benefits if people supplemented it before any signs of cognitive problems. “Vitamin D effects were significantly greater in females versus males and in normal cognition versus mild cognitive impairment,” the authors wrote.
Overall, the researchers associated vitamin D supplementation with a 40 percent lower incidence of dementia than with no supplementation.”
————————
George Citroner,
Author 1/19/2024. Updated: 1/27/2024
Article found on The Epoch Times
Hi Joyce, perfect, thank you! Linda